How Augmented Reality Is Redefining the Online Shopping Experience
In an era where e-commerce continues to grow and evolve, the introduction of augmented reality (AR) into shopping is nothing short of transformative. What once felt like science fiction — placing a virtual sofa in your living room, trying on a dress using only your phone camera, or visualizing makeup on your face in real time — is now increasingly part of the retail experience. In this article, we’ll explore how AR is changing online shopping, why it matters for consumers and retailers alike, and what the future may hold.
1. The Rise of AR in Online Retail
At its core, augmented reality overlays digital information — images, 3D models, animations — onto the real world, typically via a smartphone, tablet, or AR-enabled browser. For online shopping, this means bridging the gap between “seeing a static 2D image on a website” and “experiencing a product in your own space or on your person.”
Several forces are driving this shift:
-
Consumer demand for more immersive experience: With millions of products available online, consumers are seeking richer ways to evaluate them. One survey found that 66 % of consumers were interested in using AR in their shopping. Reydar+1
-
Technological maturation: Modern smartphones and tablets have powerful cameras, sensors and processing capability, making AR apps and browser-based AR experiences more feasible than ever.
-
Retailers’ need to reduce friction and returns: One of the major challenges of e-commerce is the inability of the consumer to physically touch or try products prior to purchase. AR helps mitigate that.
As a result, AR is no longer niche — it is becoming mainstream in online shopping, especially for categories like furniture, home décor, fashion, cosmetics and accessories. Salesforce
2. Key Benefits of AR for Shoppers and Retailers
Higher engagement and conversion
When shoppers can interact with products in a more realistic way — rotate them, place them in their space, try them on virtually — engagement rises. Studies show AR-enabled experiences can be 200 % more engaging than traditional ones.This engagement translates to higher conversion rates: retailers report that AR features can significantly increase the likelihood of a purchase. Improved visualization, confidence and fewer returns
One of the most powerful advantages of AR is helping customers visualise how a product will look in their real context. Will that sofa fit in the corner of your living room? Will that lipstick shade match your undertone? AR removes guesswork. When expectations align with reality, return rates drop. For example, retailers using AR have observed reductions in returns by double-digit percentages.
Personalisation, differentiation and brand loyalty
AR doesn’t just show a product — it can enable customisation (e.g., changing colours, finishes, textures), transforming the shopping journey into a more interactive, personalised experience. For brands, offering AR experiences signals innovation and helps differentiate them in a crowded marketplace.
Bridging online and offline
One of the persistent tensions in retail is: online convenience vs in-store tactile experience. AR helps blur that line. For example, a shopper can place a 3D model of a product in their home using their phone — effectively replicating part of the in-store experience remotely. BigCommerce
3. Real-World Use Cases That Illustrate the Shift
Here are some concrete ways AR is being applied in online shopping:
-
Furniture & Home Décor: Shoppers can place digital versions of furniture in their own rooms to check fit, scale and style. One retailer reported an 18 % lift in conversion and a 22 % drop in returns after implementing AR.
-
Fashion & Accessories: Virtual try-ons allow users to see how sunglasses, hats, shoes or jewellery will look on them. This reduces uncertainty around fit and style.
-
Beauty & Cosmetics: Using a device camera to overlay makeup shades or hair colours on the user’s face gives much better decision confidence.
-
Consumer Goods & Electronics: Letting users view products in 3D, rotate them, see them in their space, helps with understanding size, orientation and features.
4. Challenges and Considerations
While the benefits are compelling, it’s not without hurdles. Retailers and brands need to be aware of:
-
Cost and effort of implementation: Creating high-quality 3D models, AR content, integrating it into websites/apps takes time and investment.
-
Device and browser compatibility: Not all devices deliver the same AR experience. Some shoppers may have older devices or browsers that struggle with AR.
-
Accuracy and realism: If AR renders are inaccurate in scale, colour or fit, they may undermine trust rather than bolster it. Proper calibration and testing are essential.
-
User adoption and awareness: Though interest is high, not all shoppers are yet comfortable with AR. Clear guidance and intuitive interfaces help adoption.
-
Data and analytics: To fully benefit, retailers need to track how users are interacting with AR, what variants they try, and feed that back into merchandising and inventory decisions.
5. The Future of AR in Online Shopping
Looking ahead, several trends point toward deeper and broader adoption of AR in e-commerce:
-
WebAR (browser-based AR): Instead of requiring a separate app, shoppers will be able to access AR features directly via web browsers — reducing friction and increasing reach.
-
AI + AR synergy: Combined with AI, AR experiences may adapt to user preferences, suggest product variants, or customise environments in smart ways.
-
Social commerce and AR in social platforms: As social-shopping grows, AR try-ons and product visualisations will increasingly live inside social apps, making them viral and shareable. TIME
-
Wider device ecosystem: Beyond handheld devices, AR glasses or mixed-reality headsets may one day bring virtual shopping into your home in new ways.
-
Full immersion and multi-sensory experiences: Researchers are exploring immersive AR/VR that include spatial, contextual, and even olfactory or haptic feedback, although this is further off.
6. What This Means for Consumers — and You
As a shopper, here are a few takeaways:
-
Expect more brands and stores to offer AR features — especially for items where fit, size or context matter (e.g., furniture, apparel, makeup).
-
When shopping online, use AR tools (if available) to preview the product in your own environment or on your person — this can reduce post-purchase disappointment.
-
Don’t hesitate to ask for AR or 3D product viewing features if they aren’t offered — retailers may consider adding them if enough customers request them.
-
Remember: AR is a tool — it helps visualise, but you still need to check return policy, shipping, and product details.
For retailers or businesses thinking of adopting AR:
-
Start with the product categories where spatial/contextual fit is crucial (home décor, furniture, fashion accessories) — ROI is often higher.
-
Focus on quality of AR experience — realistic visuals, ease of use, quick load times. Poor AR may do more harm than good.
-
Leverage analytics from AR interactions (which variants are tried most, where users drop off) to optimise product listings and stock.
-
Consider user education and onboarding — show customers how to use AR, highlight its benefits to drive adoption.
-
Keep an eye on emerging technology (WebAR, AI integration, social AR) to stay ahead of the competition.
5 excellent examples of AR in e-commerce right now
1. IKEA — Visualising furniture in your home
One of the earlier and most recognised examples is IKEA’s AR offering. Their app (IKEA Place) allows you to place scaled 3D models of furniture in your real-room environment using your smartphone camera. Users can check how a sofa, chair or table looks and fits in their space before buying. Shopify+2ienhance.co+2
Why it matters: Furniture is one of the hardest things to buy online because size, scale and style matter so much. AR helps reduce guess-work, increase confidence and reduce returns. Forbes+1
Tip for brands / shoppers: If you’re selling furniture, plant the AR-seed here. If you’re buying, use AR tools to ensure size & style match your space.
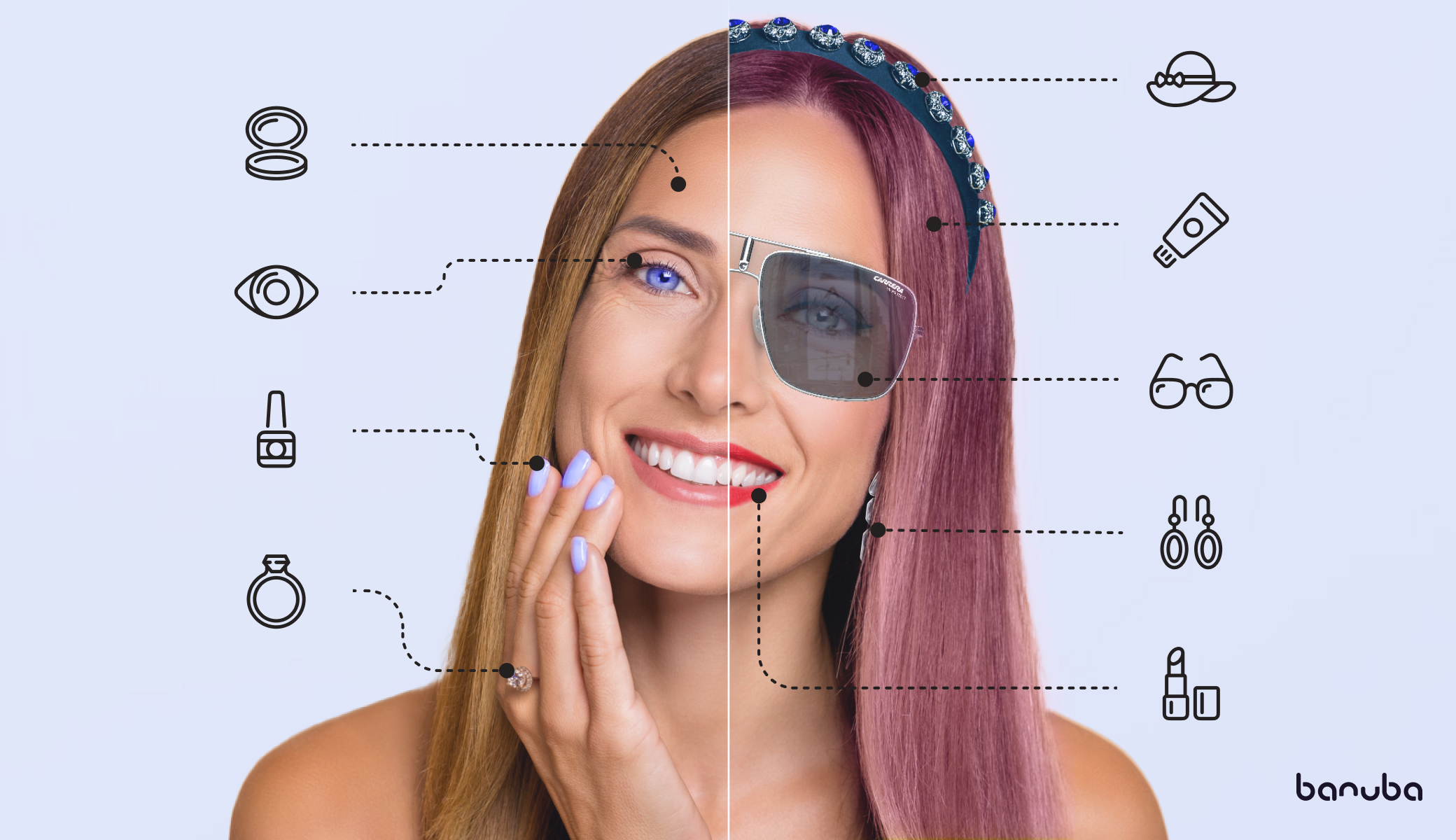
2. Sephora – Virtual makeup & beauty try-ons
Sephora has embraced AR for cosmetics: virtual try-on apps let customers apply lipstick, eyeshadow, foundation virtually, on their own face using a phone or tablet camera.
Impact: According to research, the use of virtual-try-on tools in beauty has driven conversion lifts (one case study notes ~ 35 % increase in conversions) when customers use AR features.
Tip: For beauty/fashion brands: offering virtual try-ons can massively boost confidence and engagement. For shoppers: try the virtual option to see how a product might look on you before buying.
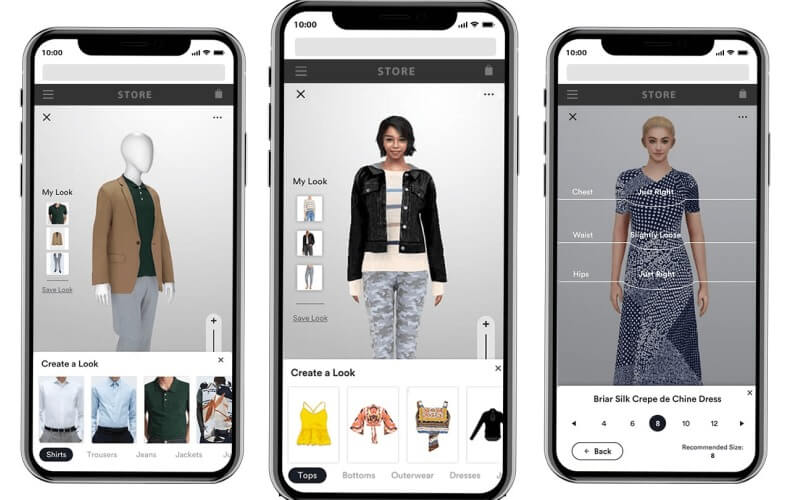
3. Apparel & Virtual Fitting Rooms – example from Walmart
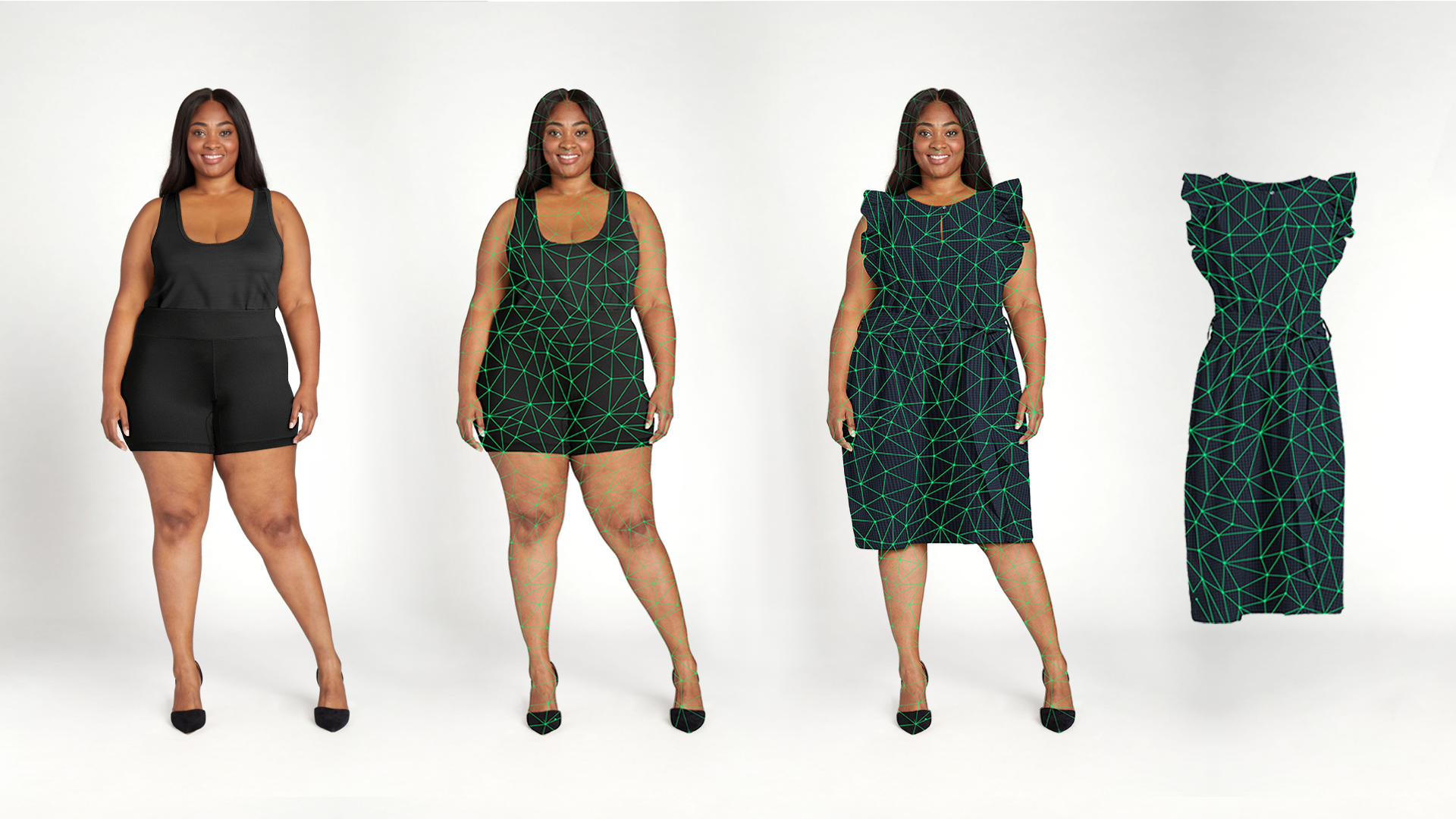
In the apparel category, one of the use-cases of AR is virtual fitting rooms: enabling the online shopper to “try on” clothing items virtually. For example, Walmart introduced a virtual try-on tool that aligns with body-type, etc.
Why it’s important: Fit & style are among the biggest pain-points of online apparel shopping (leading to high return rates). Virtual try-on reduces uncertainty.
Tip: If you’re shopping for clothes online, look out for sites that offer virtual fitting/try-on — it may save you hassle and returns.
4. Specialty Furniture & Home-Decor Retailers – e.g., web-native AR
Beyond big players, many furniture/home-decor retailers are now offering “view in your room” AR features via the web (not always an app). For example, research shows brands are offering AR directly from website without requiring app downloads.
Benefit: Lower friction (no app download), more seamless online shopping, helping shoppers visualise one-off pieces in their space.
Tip: If you’re browsing home-decor items, try to use any “view in room” AR features and compare how it looks with your current space or décor.
5. Broad AR Use-Cases Across E-commerce (Beauty, Furniture, Accessories)
According to wider research, AR in e-commerce is not just limited to one category — it spans furniture, beauty, accessories, home décor and more. VNTANA | 3D Content Management System”+1
For example: Accessories like sunglasses, hats, jewellery can be “tried on” virtually; home décor items can be placed in a room; beauty products can be applied to a virtual face.
Tip: Even if a retailer doesn’t advertise AR prominently, you might find hidden AR features (e.g., “View in your room”, “Try on virtually”) — it’s worth giving them a try.
Conclusion
The integration of augmented reality into online shopping is more than a novelty — it’s a meaningful shift in how consumers interact with products and brands. By bridging the experiential gap between “online” and “in-store,” AR is empowering shoppers with confidence, reducing returns, increasing engagement and helping retailers differentiate themselves.
While challenges exist — cost, device compatibility, realism — the advantages are compelling and the trajectory is clear: AR will increasingly be a standard part of the online shopping toolbox. Whether you’re a consumer leaning into new shopping tools, or a retailer plotting your next innovation, AR deserves attention.
The question is no longer “Will AR change online shopping?”, but “How quickly will your brand adopt it — and how will you as a shopper leverage it?”